Analysis and Simulation of Multi-Detachment Fold-Thrust Structures - Taking the Majiaba Fault in the Longmen Shan Fault as an Example
Paper Download:
Title:Analysis and Simulation of Multi-Detachment Fold-Thrust Structures - Taking the Majiaba Fault in the Longmen Shan Fault as an Example
Author:Yanjie Feng
Abstract
Based on discrete element numerical simulation technology, this paper designs multiple sets of 2D horizontal compression experiments to simulate the formation and evolution processes of multi-detachment fold-thrust belts. It analyzes the deformation mechanisms of multi-detachment fold-thrust belts and draws the following conclusions:
1.The stress deformation of gypsum-salt detachment layers is mainly plastic rheology, often exhibiting strong bulk strain and shear strain, but no faults develop internally. 2.The position and thickness of detachment layers can affect the distribution of stress and strain in fold-thrust belts. Among them, the basal detachment layer is the main factor influencing the overall structural evolution. 3.The discrete element numerical simulation method can, to a certain extent, quantitatively explain the evolution processes and deformation mechanisms of fold-thrust structures, showing good development prospects.
Keywords: Detachment Layer; Discrete Element Model; Fold-Thrust Belt; Structural Deformation
Table of Contents:
- Chapter 1 Introduction
- 1.1 Significance of Research and Basis for Topic Selection
- 1.2 Current Status of Quantitative Research on Structural Deformation
- 1.3 Innovations
- Chapter 2 Methodology Overview
- 2.1 Introduction to Discrete Element Method
- 2.2 Introduction to VBOX Software
- 2.3 Introduction to Hertz-Mindlin Contact Model
- 2.4 Stress-Strain Analysis
- Chapter 3 Numerical Simulation Experiments
- 3.1 Experiment 1 Without Gypsum-Salt Layer
- 3.2 Experiment 2 With Gypsum-Salt Layer at the Bottom
- 3.3 Experiment 3 With One Gypsum-Salt Interlayer
- 3.4 Experiment 4 With Two Gypsum-Salt Interlayers
- 3.5 Experiment 5 Changing the Thickness of Gypsum-Salt Layer
- 3.6 Experiment 6 Boundary Extension Experiment
- 3.7 Experiment 7 Changing the Density of Detachment Layer
- Chapter 4 Discussion: Comparison with Majiaba Fault in Longmen Shan Fault
- Chapter 5 Conclusions
- References
Conclusions
Based on the experimental results and analysis of actual conditions, we can draw the following main conclusions:
- The deformation of the gypsum-salt detachment layer is mainly plastic rheology, with no faults developing internally, and significant bulk strain and shear strain are observed.
- The thickness, density, and distribution of the detachment layer significantly affect the propagation and distribution of stress and strain. In terms of horizontal propagation, the detachment layer makes it easier for stress and strain to propagate. Vertically, the detachment layer is a key factor in the vertical stratification of deformation, with distinct structural deformation patterns above and below the detachment layer. The presence of double detachment layers accelerates the propagation speed of stress and strain and also affects the maximum propagation distance.
- The complex structures in the Majiaba area of the Longmen Shan Fault in Sichuan may be influenced by double detachment layers, driven by two phases of tectonic geological movements: gravitational detachment and regional horizontal compression.
- VBOX software can be effectively used to simulate fold-thrust structural deformation, and the simulation results show a good agreement with actual geological structures. Additionally, VBOX software is equipped with various basic model data, along with its open multi-port design and efficient parallel computing design, demonstrating good potential in tectonic geological simulation. With continuous updates in computing hardware and software facilities, tectonic numerical simulation will have broader development prospects.
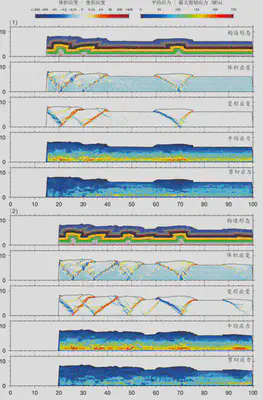
Experiment 6
Translator: Ouyang Liujuan