Influence of Regional Erosion and Sedimentary Loading on Fault Activities in Active Fold-Thrust Belts
Title
Influence of Regional Erosion and Sedimentary Loading on Fault Activities in Active Fold-Thrust Belts: Insights From Discrete Element Simulation and the Southern and Central Longmen Shan Fold-Thrust Belt
Authors
Wu Z1,2, Yin H3, Li C1,2, Yang X2, Wang L2, Wang F2, Dong S3 and Jia D3
- State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resources and Environment, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, China
- School of Earth Sciences, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, China
- School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China
Abstract
Four groups of discrete element models (DEMs) were set-up to simulate and analyze the influence of regional erosion and sedimentary loading on the formation and spatial-temporal evolution of faults in the southern and central Longmen Shan (LMS) active fold-thrust belt. The interior characteristics of faults in the southern and central LMS fold-thrust belt were also evaluated during the interaction of tectonic processes and surface processes according to the stress-strain analysis from DEM results. The results showed that synkinematic erosion promoted the reactivation of pre-existing faults in thrust wedges and also retarded the formation and development of new incipient faults in the pre-wedge regions. Meanwhile, synkinematic sedimentation also delayed the development of new incipient faults in the pre-wedge regions by promoting the development of thrust faults in the front of thrust wedges, causing these thrust wedges in supercritical stages with relatively narrow wedge lengths. According to these DEM results, we infer that: 1) The characteristics of erosion and sedimentation in the central and southern LMS have important influences on the activities of large faults which are extended into the deep detachment layer; 2) Besides differential erosion, the differential sedimentary loading may also be one of the important factors for the along-strike differential evolution of the LMS fold-thrust belt. This kind of differential deposition may lead to differential fault activity and uplift in the interior thrust wedge and pre-wedge region in the central and southern LMS; 3) Compared to the northern LMS, the central LMS and southern LMS is more conducive to the occurrence of earthquakes, because of synkinematic sedimentation (such as the growth of Chengdu plain) has a greater blocking effect on the stress propagation and strain convergence on the fault planes of front faults of an active thrust wedge.
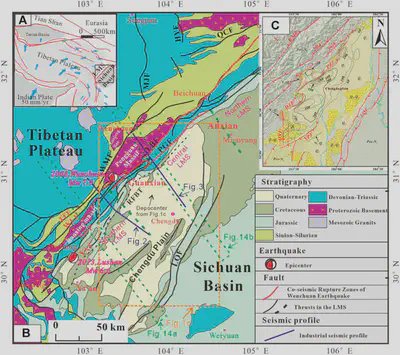
FIGURE 1 | Regional map of the LMS fold-thrust belt (A) and its geological structure map (B) (modified from [(Sun et al.,2016)](#refer-sun2016), Co-seismic rupture zones from [(Xu et al.,2009)](#refer-xu2009). (C) shows the thickness contour lines (100 m interval) of the Upper Pliocene and Quaternary (syntectonic sedimentary strata) beneath the Chengdu plain (cited from [(Li et al.,2018)](#refer-li2018). JTF, Jintang Fault; WLF, Wulong Fault; WMF, Wenxian-Maoxian Fault; SDF, Shuangshi-Dachuan Fault; PGF, Pengxian-Guanxian Fault; YBF, Yingxiu-Beichuan Fault; YAF, Yaan Fault; LQF, Longquanshan Fault; QCF, Qingchuan Fault; MJF, Minjiang Fault; HYF, Huya Fault; RFBT, Range Front Blind Thrust.
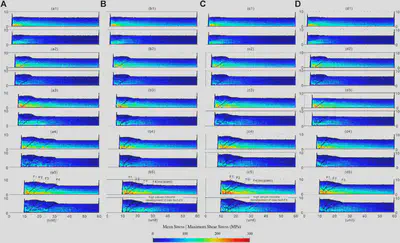
FIGURE 10 | Stress analysis of DEM simulations in Model 1 (A), Model 2 (B), Model 3 (C), and Model 4 (D). Mean stress (upper figure) and maximum shear stress (lower figure) are presented after every 2 units shortening. The main fault shapes (shades of black) are assigned to the stress maps.
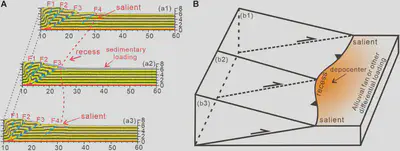
FIGURE 13 | The DEM results in this paper (A) and the conceptual model modified from Liu et al., 2020(B) present the occurrence of recess and salient in the front of thrust wedges.
References
Li, Z., Zhang, P., Zheng, W., Jia, D., Hubbard, J., Almeida, R., et al. (2018b). Oblique Thrusting and Strain Partitioning in the Longmen Shan Fold-Andthrust belt, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 123, 4431-4453. doi:10.1029/2018JB015529 Sun, C., Jia, D., Yin, H., Chen, Z., Li, Z., Shen, L., et al. (2016). Sandbox Modeling of Evolving Thrust Wedges with Different Preexisting Topographic Relief: Implications for the Longmen Shan Thrust belt, Eastern Tibet. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 121, 4591–4614. doi:10.1002/2016jb013013 Xu, X., Wen, X., Yu, G., Chen, G., Klinger, Y., Hubbard, J., et al. (2009). Coseismic Reverse- and Oblique-Slip Surface Faulting Generated by the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan Earthquake, China. Geology 37 (6), 515–518. doi:10.1130/g25462a.1Translator: Ouyang Liujuan